Non-conformance Management Software
Non-conformance issues can arise in any stage of production, from internal processes to supplier and customer interactions. Managing these issues efficiently is critical to ensuring product quality, maintaining compliance, and minimizing downtime. With our Non-Conformance Management Software, you can quickly identify, track, and resolve non-conformance events across your organization, ensuring smoother operations, higher quality standards, and improved regulatory compliance.

Benefits of Our Non-Conformance Management Software
A Specialized Software To Help You Manage Non-Conformance
Centralized Tracking
Track and manage non-conformance events across your organization in one unified system. Whether the non-conformance is internal, from a customer, or from a supplier, our software gives you complete visibility.
Automated Workflow
Automate key processes such as notifications, approvals, and task assignments. Email alerts keep everyone informed of critical developments, ensuring swift resolution of issues.
Root Cause Analysis
Identify the root causes of non-conformances with built-in tools for performing root cause analysis. By addressing the underlying causes, you can prevent future issues and improve overall product quality.

CAPA Management
Ensure both corrective and preventive actions are taken when non-conformances occur. Track the effectiveness of CAPAs over time and close the loop on problem-solving.

Non-Conformance Reporting & Tracking
The NCR system simplifies reporting, tracking, and resolving non-conformances, ensuring compliance, accountability, and timely corrective actions with automated notifications.

Compliance Tracking
Stay on top of your regulatory obligations with built-in compliance tracking features. The software helps you maintain adherence to standards like ISO, FDA, GMP, and more, through automated audit trails and compliance reporting.
QISS QMS Ensure Your System Comply with Industry Standards
Who Can Use This Software?
Our Non-Conformance Management Software is built to meet the needs of key personnel in quality management and production teams:
-
Quality Managers: Take control of your organization’s non-conformance events and drive compliance with regulatory requirements.
-
Production Managers: Track and resolve quality issues in production quickly to minimize delays and maintain operational efficiency.
-
QC/QA Technicians: Log non-conformance events accurately and provide essential data for root cause analysis and corrective actions.
-
Root Cause Analysis Specialists: Identify, analyze, and eliminate the causes of non-conformances to prevent future issues.
-
CAPA Coordinators: Ensure that corrective and preventive actions are defined, tracked, and closed out effectively.
-
Regulatory Affairs Managers: Ensure that your company is meeting all industry regulations and standards, keeping your organization audit-ready at all times.
-
For Everyone Committed to Quality: You don’t need a specific job title to benefit from this software. If you wish to improve quality, productivity and profitability, you should use this Non-Conformance Management Software to ensure that you follow best industry practices.

Key Features of Our Non-Conformance Management Software
Our Non-Conformance Management System is more than just a tracking tool—it’s a robust, configurable solution designed to improve your quality management processes, ensure compliance, and provide deeper insights into your operations.
Our non-conformance software is built with role-based permissions to ensure that only authorized users can perform specific activities. This enhances security, reduces the risk of errors, and ensures that critical tasks are performed by the right people. Module managers or authorized personnel control who can initiate, approve, or edit non-conformance records (NCRs), ensuring clear accountability.
Our system allows you to initiate NCRs from multiple origins — whether internal, customer-related, or supplier-driven. This flexibility ensures that you can capture non-conformance events from all areas of your business, improving oversight. Additionally, the Non-Conformance system offers customization options so you can tailor the software to your specific needs, from default settings to workflow processes.
Easily associate each NCR with a category and failure mode. Disposition types are defined by category, ensuring each non-conformance is categorized properly for analysis. This streamlines the investigation process and ensures that corrective actions are targeted and effective. Plus, you can reference and link multiple NCRs to track related events and their resolutions.
Resolve Issues Before They Escalate With Automated Workflow
Our Non-Conformance management system will help you proactively identify and address issues with automated workflows. So you can ensure timely corrective actions and prevent escalation to improve operational efficiency and compliance.
Our NCR Management Workflow Procedure
Check our procedure step by step
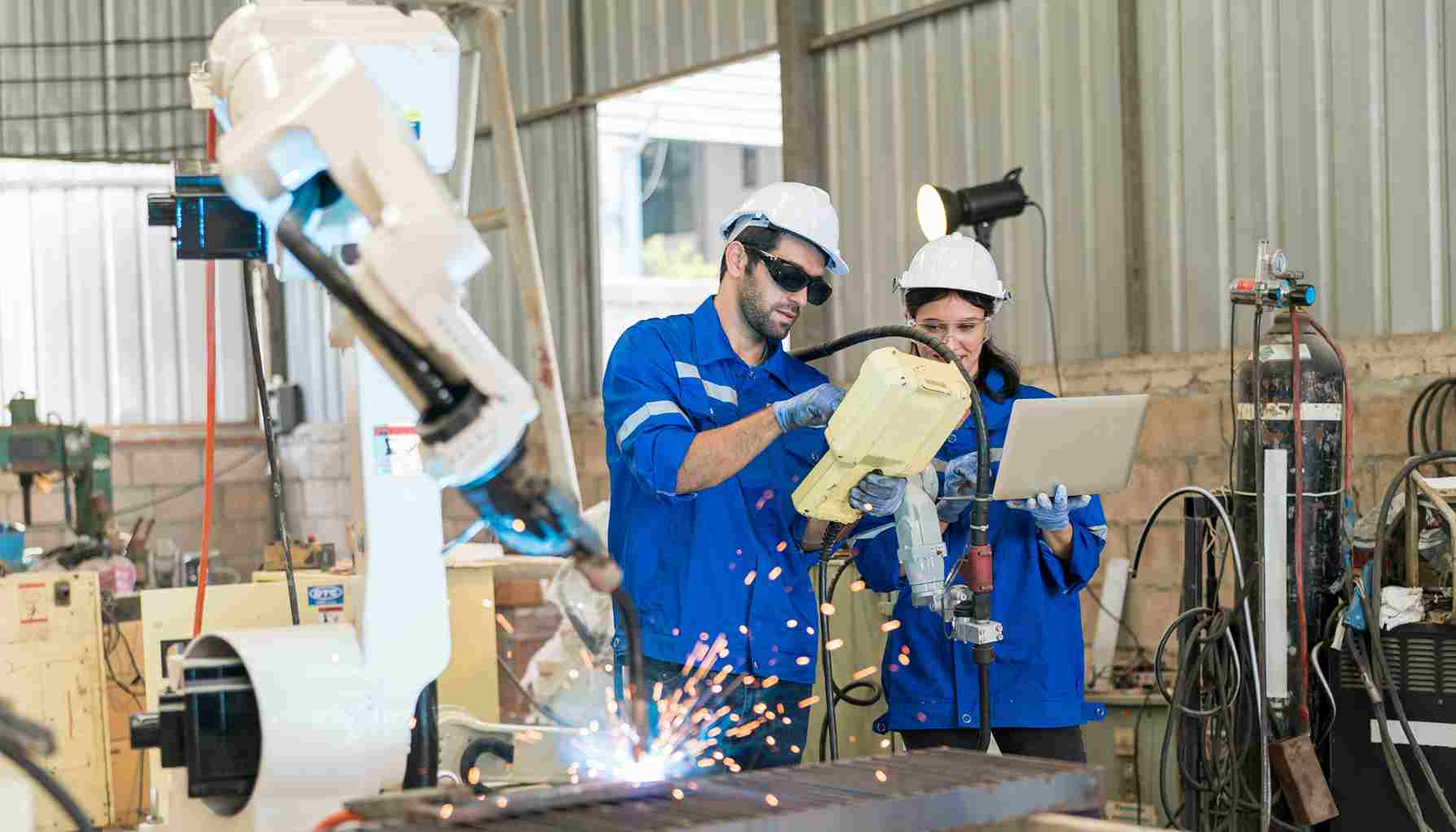












For Manufacturing
Nonconformance management software in manufacturing helps track product and process deviations by automating reports, assigning corrective actions, and ensuring timely resolution. It centralizes data, improves traceability, and improves decision-making by providing real-time insights into quality issues. This reduces downtime, waste, and ensures consistent product quality, boosting efficiency.
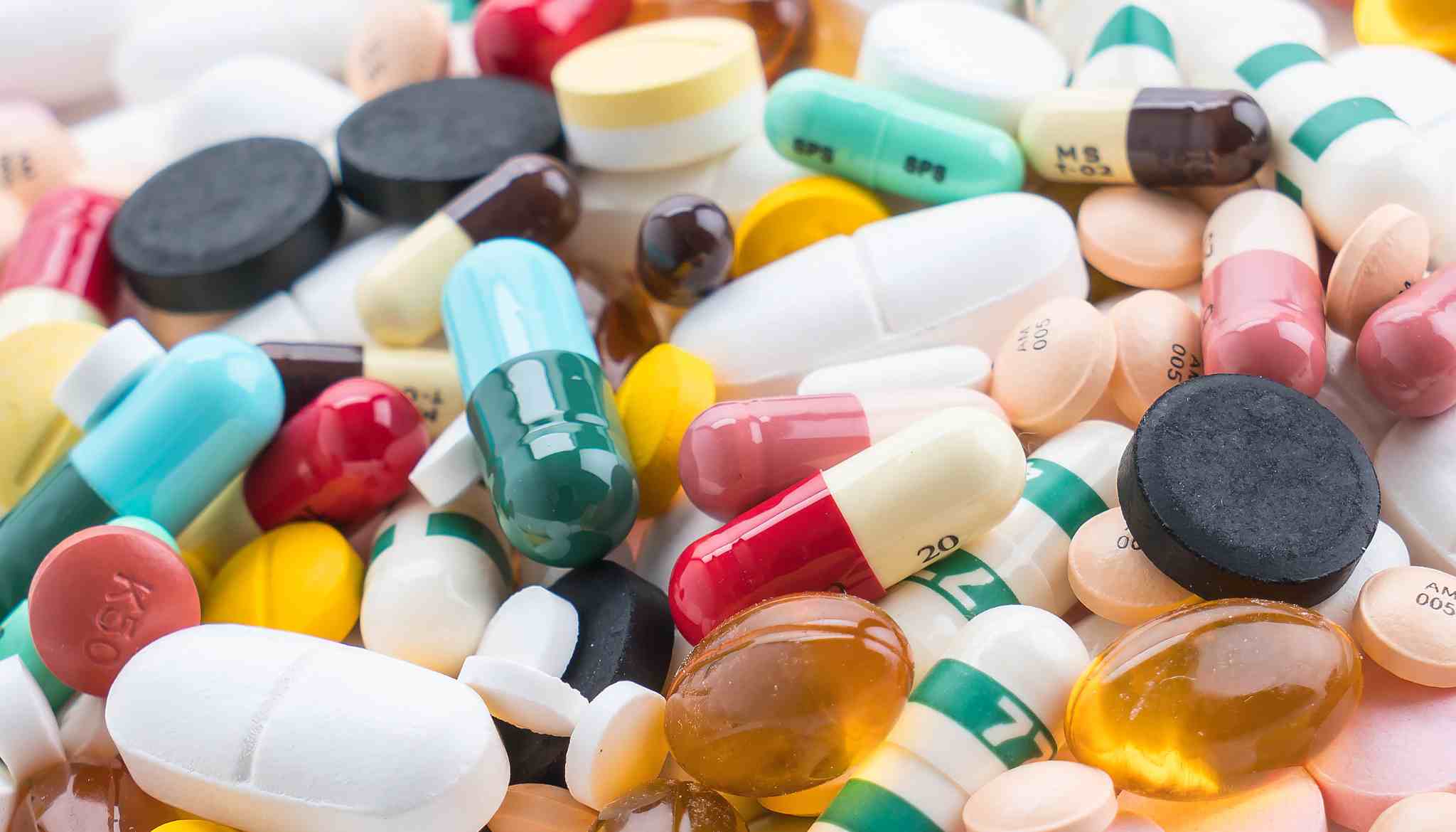

For Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, nonconformance management software ensures compliance with regulatory requirements (e.g. FDA, GMP). It helps track deviations, document investigations, and monitor corrective actions. By automating workflows and providing audit trails, the software reduces the risk of non-compliance, prevents costly recalls, and improves product quality and regulatory readiness.
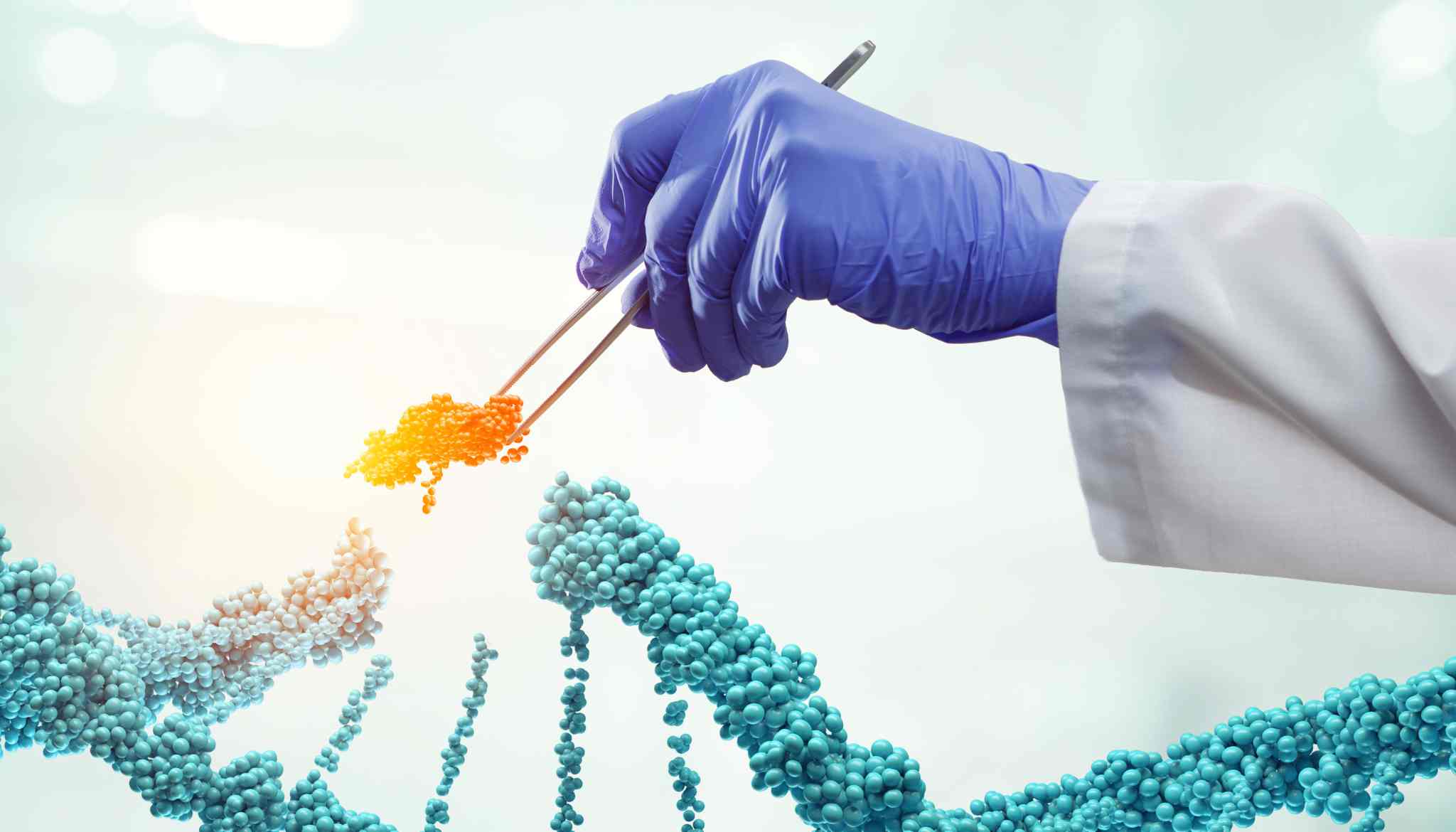

For Biologics Industry
For biologics, nonconformance management software tracks deviations from production to final product release. It streamlines root cause analysis, automates corrective actions, and supports regulatory documentation. This software enhances product safety, ensures batch consistency, and reduces the risk of regulatory non-compliance, improving overall efficiency.
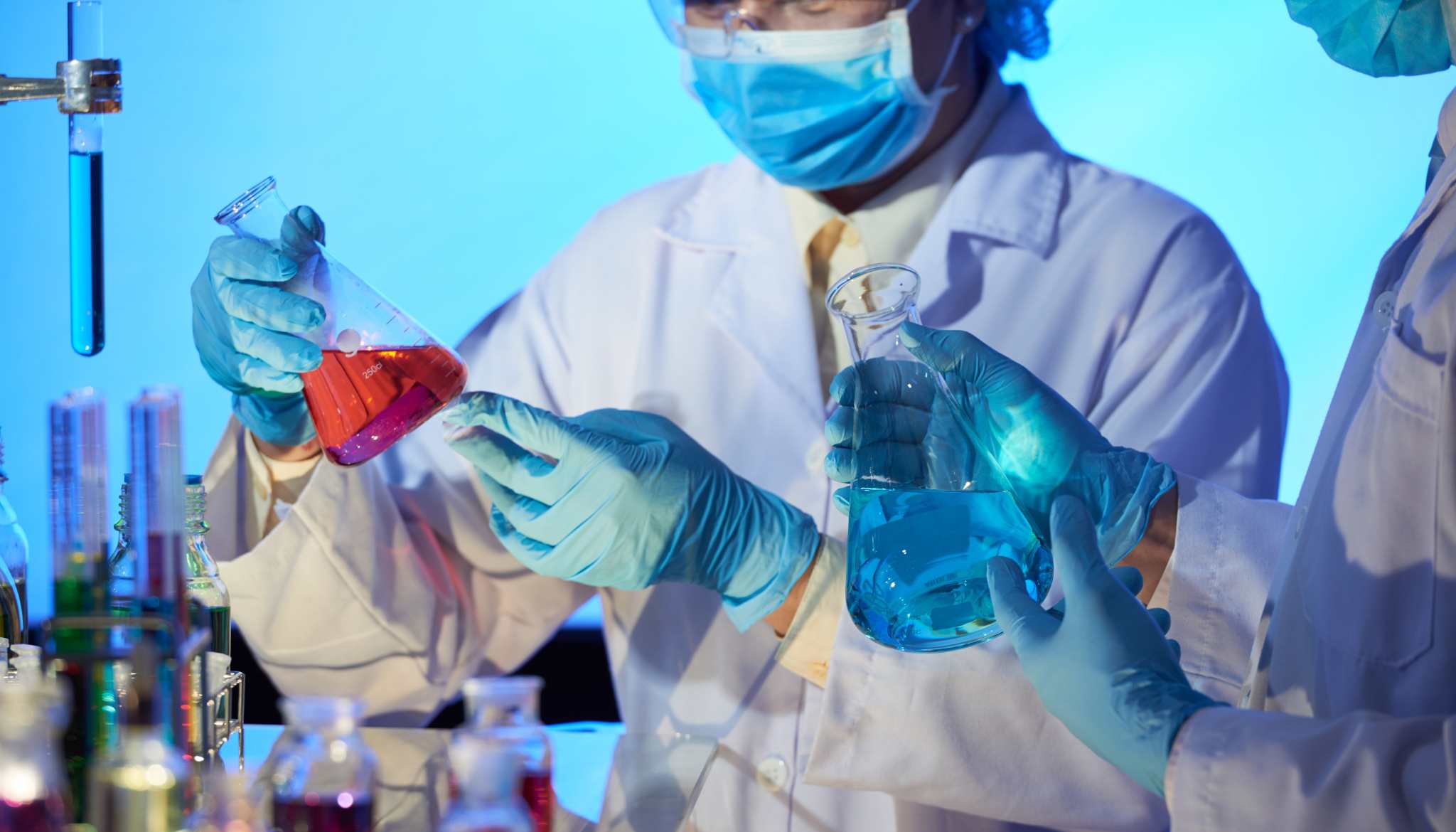

For Chemical Industry
This software manages non-conformances in raw materials, production, and testing in the chemical industries by automating reporting, root cause analysis, and corrective actions. It helps ensure compliance with environmental, safety, and regulatory standards (e.g. REACH, EPA), reduces risks, and ensures product integrity, thereby enhancing quality control and operational efficiency.
About QIA
Founded in 1994 in Houston, Texas, the Quality Institute of America (QIA) originally focused on consulting, auditing and training for quality management based on ISO standards and requirements. Today, we specialize in software development to help clients improve profitability through effective management systems. Our QISS products automate workflows to ensure compliance and efficiency across various management systems and global regulations.

Years of Experience

ISO Trainer

ISO Consultants

Internal ISO Auditor

Customer Support
Testimonials
What Our Clients Say About Us
Our Clients













Frequently Asked Questions
A marine surveyor inspects ships, cargo, and equipment to ensure safety, compliance, and condition. They specifically inspect cargo tanks and holds for the acceptability of cleaning from prior cargo before new cargo is loaded, particularly for sensitive chemical cargo. Marine surveyors also witness cargo loading, perform cargo sampling, and oversee cargo tank sealing to ensure proper handling and compliance with regulatory standards.
Understanding of cargo loading, stowage, securing practices, and international regulations related to cargo handling. Surveyors also investigate cargo damage claims and develop loss prevention strategies.
Learning Center
Here, you will find articles related to different aspects of a Quality Management and Laboratory Management System. This is a center for gaining knowledge.













